Large Language Models (LLMs) like GPT-4, Claude, and Gemini are incredibly powerful, but what if you want your model to sound like your brand, understand your documents, or perform your specialised tasks?
Page Contents
That’s where fine-tuning comes in. Fine-tuning lets you train an existing LLM on your own data, giving it new domain knowledge or a unique conversational style, without starting from scratch. And the best part? You can do it on a budget, thanks to open-source models like LLaMA 3, Mistral, Falcon, and Gemma, combined with lightweight techniques like LoRA and QLoRA.
In this step-by-step guide, you’ll learn how to fine-tune an open-source LLM on your own dataset — affordably and effectively.
Why Fine-Tune Instead of Starting Fresh?
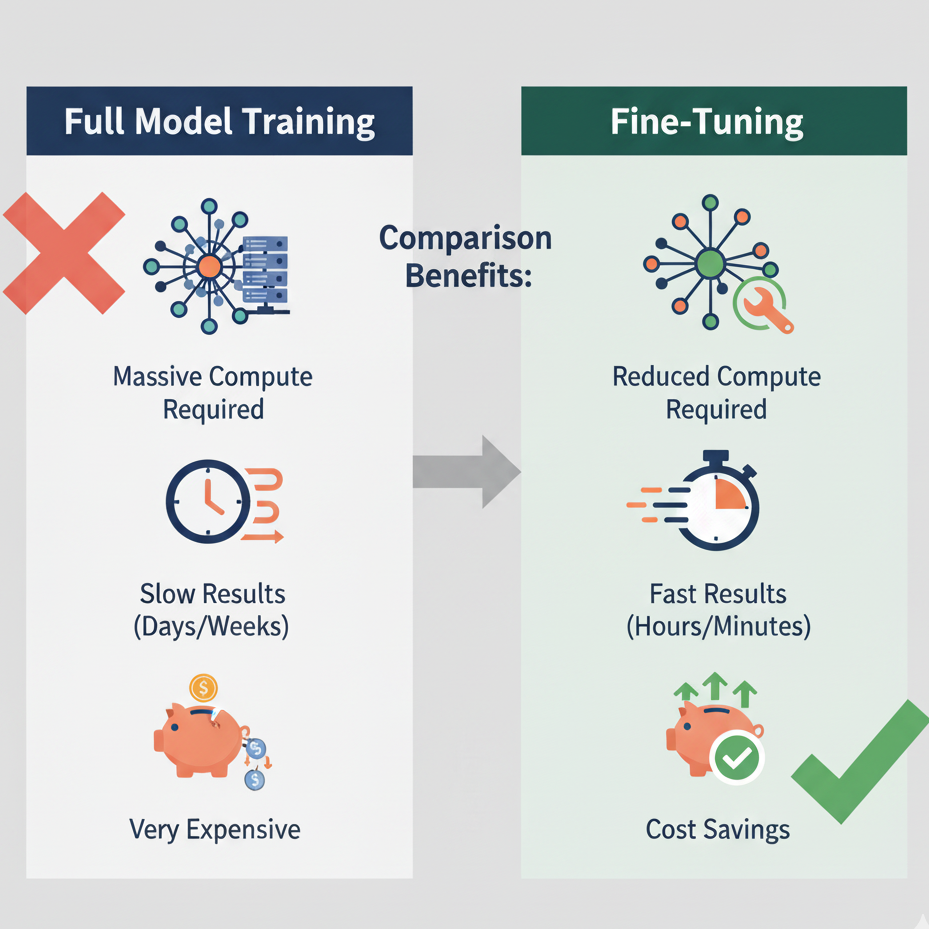
Training an LLM from scratch can cost millions in GPU hours and data collection. Fine-tuning, on the other hand, is like giving an already-trained model a “masterclass” in your specific domain.
For example:
- A healthcare startup can fine-tune an LLM on medical research papers.
- A SaaS company can fine-tune it on customer support tickets.
- A marketing team can fine-tune it on brand tone and writing style.
This results in faster, cheaper, and highly targeted performance.
Step 1. Choose Your Base Model
You’ll want an open-source model that fits your hardware and target use case. Here are a few great starting points:
| Model | Size | Ideal Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| LLaMA 3 (Meta) | 8B–70B | General-purpose reasoning |
| Mistral 7B | 7B | Fast, efficient, and multilingual |
| Gemma (Google) | 2B–7B | Lightweight and easy to deploy |
| Falcon 7B | 7B | Open-weight, strong for instruction tuning |
For this walkthrough, we’ll use Mistral 7B, as it’s small, powerful, and freely available on Hugging Face.
Step 2. Prepare Your Custom Dataset
Fine-tuning data is typically in JSONL (JSON Lines) format, where each line contains an instruction, input, and output.
Example:
{"instruction": "Summarize the following article.", "input": "The Indian space program achieved...", "output": "ISRO successfully completed..."}
{"instruction": "Answer customer query about billing", "input": "How can I update my payment method?", "output": "You can update it under Account > Billing Settings."}
👉 Keep your data clean, concise, and aligned with the task you’re optimising for (e.g., summarisation, Q&A, dialogue).

Step 3. Environment Setup
Install the required dependencies:
pip install transformers datasets peft bitsandbytes accelerate
transformers: Core model interfacedatasets: For loading your datasetpeft: For efficient fine-tuning using LoRAbitsandbytes: Enables quantised training (saves GPU memory)accelerate: Handles distributed/optimised training
Step 4. Load the Model and Tokeniser
You can load the base model from Hugging Face easily:
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
model_name = "mistralai/Mistral-7B-v0.1"
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
model_name,
load_in_8bit=True,
device_map="auto"
)
This loads the model efficiently in 8-bit precision, significantly reducing GPU usage.
Step 5. Apply LoRA for Efficient Fine-Tuning
Instead of modifying all parameters, LoRA (Low-Rank Adaptation) adds a few small trainable layers on top of the base model, drastically reducing cost and time.
from peft import LoraConfig, get_peft_model
lora_config = LoraConfig(
r=16,
lora_alpha=32,
target_modules=["q_proj", "v_proj"],
lora_dropout=0.05,
bias="none",
task_type="CAUSAL_LM"
)
model = get_peft_model(model, lora_config)
Step 6. Load Your Dataset
Load your prepared JSONL dataset:
from datasets import load_dataset
dataset = load_dataset("json", data_files="custom_data.jsonl")
train_data = dataset["train"].shuffle(seed=42)
Step 7. Fine-Tune the Model
Now, it’s time to train:
from transformers import TrainingArguments, Trainer
training_args = TrainingArguments(
output_dir="./mistral-finetuned",
per_device_train_batch_size=4,
gradient_accumulation_steps=4,
learning_rate=2e-4,
num_train_epochs=3,
fp16=True,
logging_steps=50,
save_total_limit=2
)
trainer = Trainer(
model=model,
args=training_args,
train_dataset=train_data
)
trainer.train()
This setup utilises mixed precision (FP16) and LoRA to accelerate training and reduce costs, even on a single GPU like the RTX 3090.
Step 8. Test Your Fine-Tuned Model
After training, you can test how well it performs:
prompt = "Explain the refund process in simple terms."
inputs = tokenizer(prompt, return_tensors="pt").to("cuda")
outputs = model.generate(**inputs, max_new_tokens=150)
print(tokenizer.decode(outputs[0], skip_special_tokens=True))
Compare outputs before and after fine-tuning. You’ll notice how your model becomes more domain-specific and natural for your use case.
Step 9. Optimise for Cost
Fine-tuning doesn’t need expensive infrastructure.
Here are a few low-cost strategies:
- Use LoRA/QLoRA instead of full fine-tuning.
- Run on Google Colab Pro, Lambda Cloud, or RunPod.
- Use 4-bit quantisation (
bnb_4bit=True) for smaller GPUs. - Fine-tune fewer epochs with high-quality data.
Even with a $20–$50 GPU rental, you can achieve excellent specialised results.
Step 10. Save and Deploy Your Model
Once trained, you can push your model to Hugging Face or run it locally:
model.push_to_hub("your-username/mistral-custom-finetuned")
tokenizer.push_to_hub("your-username/mistral-custom-finetuned")
Or, integrate it directly with LangChain or a FastAPI endpoint to build your custom AI app.
Final Thoughts
You’ve just fine-tuned an open-source LLM on your own data, without massive costs or a data centre! With LoRA and tools like Hugging Face Transformers, customising AI for your business or project has never been easier. Whether you’re building a medical assistant, a legal chatbot, or a brand voice generator, fine-tuning puts true personalisation within reach.
Recommended Resources
- Hugging Face Transformers Docs
- PEFT (Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning)
- Mistral 7B Model Card
- QLoRA Paper (2023)
Parvesh Sandila is a results-driven tech professional with 8+ years of experience in web and mobile development, leadership, and emerging technologies.
After completing his Master’s in Computer Applications (MCA), he began his journey as a programming mentor, guiding 100+ students and helping them build strong foundations in coding. In 2019, he founded Owlbuddy.com, a platform dedicated to providing free, high-quality programming tutorials for aspiring developers.
He then transitioned into a full-time programmer, where his hands-on expertise and problem-solving skills led him to grow into a Team Lead and Technical Project Manager, successfully delivering scalable web and mobile solutions. Today, he works with advanced technologies such as AI systems, RAG architectures, and modern digital solutions, while also collaborating through a strategic partnership with Technobae (UK) to build next-generation products.
